
Most of us spend time on our mobile tablets or phones before we go to sleep. The problem with that is we end up dealing with lots of blue light exposure. But why is this blue light a concern? Does blue light affect sleep?
In this article we will focus on why blue light is bad for sleep, how the light that is shining in our face at bedtime may be preventing us from getting restful and restorative sleep, and on some things we can do to solve this problem.
What is blue light?
Visible to the human eyes is a band of wavelengths called the visible light spectrum.
The image below shows the visible light spectrum.
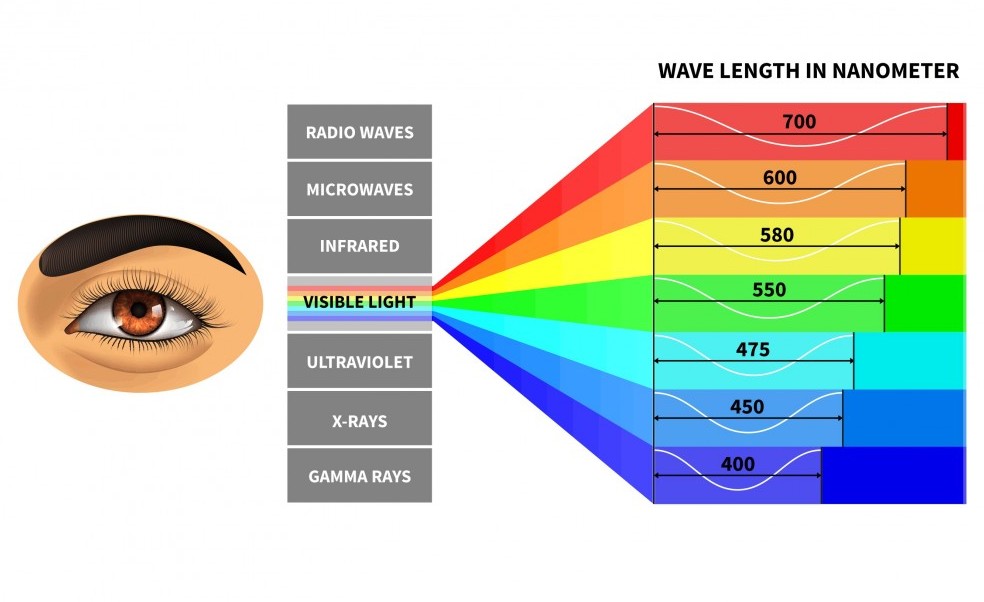
Visible light is seen as colors, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Blue light is the portion of the visible light spectrum, spanning from 380 to 500 nanometers (nm).
Blue light has a wavelength that is very short, and so produces a higher amount of energy.
Blue light affects levels of melatonin more than any other wavelength does.
Sources of Blue Light
Our main source of blue light is sunlight. Blue light from the sun in the daytime is beneficial as it helps improve your alertness, performance, and mood.
At night, however, blue light is emitted from devices, such as our mobile smart-phones and tablets, computer screens, digital clocks, hand-held video game devices, televisions, and even indoor lighting such as fluorescent light bulbs and LED lights.
Why is blue light bad for our sleep?
This all relates to the melatonin levels in our body.
Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the body’s circadian rhythm, the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Melatonin levels are low during the day and then they are higher during the night as you prepare to go to sleep.
A problem occurs when we use our screens at night.
Blue light emanated by your gadgets will suppress the melatonin levels. As a result, you may not fall asleep easily.
Your brain will end up thinking that it’s still light outside, so you need to sleep later.
Blue light reduces both the quantity and quality of your sleep.
Obviously this has a negative impact on your sleep and the way you rest and morning alertness.
And that’s the type of thing you want to avoid.
Protecting yourself from blue light
Good sleep is essential for attention, learning, mood, and general well-being.
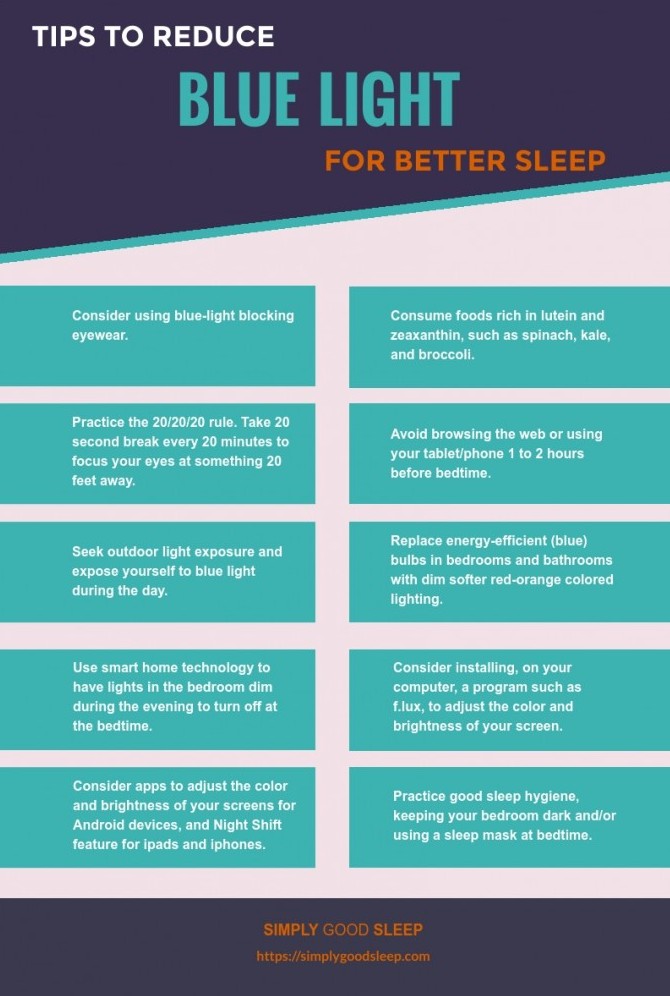
There are several ways you can protect yourself from blue light for better sleep and better eye health:
Use blue light blocking eyewear
Blue-light-blocking eyeglasses, worn in the evening near bedtime, may filter blue light from electronic devices, increasing melatonin production and leading to better sleep.
Consume foods that are rich in zeaxanthin and lutein
Zeaxanthin and lutein can be found in foods which include leafy green vegetables (such as spinach and kale) and other colorful fruits and vegetables (such as broccoli, kiwi fruit, tangerine). These foods may help to alleviate the harmful effects of blue light.
20/20/20 rule
It’s also a good idea to use the 20/20/20 rule when looking at the screens of electronic devices. You need to take a 20 second break every 20 minutes and have your eyes focus at something 20 feet away. This will lower eye strain, prevent headaches, help relax your mind, and may help you fall asleep easily.
Cyber curfew before bed
If possible, avoid browsing the web or using your tablet/phone right before you sleep. In fact, tuck these devices away 1 to 2 hours before you go to sleep to enable your body to produce more melatonin and to help your brain wind down for sleep.
Blue light exposure earlier in the day
Seek outdoor light exposure and expose yourself to blue light in the early hours of the day.
Use sleep-friendly lighting
Replace energy-efficient (blue) bulbs in bedrooms and bathrooms with dim softer red-orange colored lighting. Red light has a higher wavelength and does not significantly suppress melatonin production.
Leverage smart technology
Consider using smart home gadgets to have lights in the bedroom or in the home dim in the evening to turn off at the scheduled bedtime.
Computer screen filters
Consider installing, on your computer, a program called f.lux, which enables you to adjust or preset the color and brightness of your screen. When it is dark outside, the program can filter blue light and give your screen an orange hue.
Use filter apps
Similar apps are available for your Android smartphone and mobile tablets. Night Shift feature is available for ipads and iphones.
Good sleep hygiene
Practice good sleep hygiene, keeping your bedroom dark and/or using a sleep mask at bedtime.
Final Words
Blue light, emitted from electronic devices, such as computers, tablets, smart-phones, may inhibit your sleep if you’re exposed to it in the evening close to bedtime.
If you have a history of experiencing difficulty falling asleep at night, consider reducing your exposure to blue light in the evening.
Potential long term eye damage from ongoing exposure to blue light is also not something to play with, so do everything you can to protect your eyes and to get simply good sleep!

2 Responses
The yellow tinted glasses worn 2-3 hours just before bed have helped me to fall asleep more easily. I think in general, we wear our eyes out all day with the phones, computer, tv and then at night they STILL don’t get a break from all the blue light so anything you can do to reduce it will help. It’s also good for your mind to relax before bed, it isn’t good to be mentally stimulated every waking hour.
That’s right! Have a cyber curfew before bedtime! Turn off your electronics – for example, smartphones, laptops, tablets, e-readers, TVs, and gaming devices – around 2 hours prior to bedtime. The screens of these devices emanate blue light that can prevent you from falling asleep and getting good sleep.